Vue 组件渲染机制
以下示例代码基于 vue3.0、vue3.2(后续修改)
任何前端框架,最主要的核心功能就是渲染视图。在 Vue 中,整个应用的页面都是通过组件来构成并渲染成页面。
在了解 vue 组件之前,先了解 VirtualDOM(在 vue 中则称为 vnode)。
VNode
Vue 的渲染原理中使用 VirtualDOM 机制,VirtualDOM 本质上是用来描述真实 DOM 的 JavaScript 对象。
我们可以用一个 vnode 对象去表示<button>节点。一个 VNode 的属性最主要的是节点类型 type,节点属性 props,字节点 children。
<button class="btn" style="width:100px;height:50px">click me</button>
const vnode = {
type: "button",
props: {
class: "btn",
style: {
width: "100px",
height: "50px",
},
},
children: "click me",
};
引入 VNode 的好处:
- 任何常规的 GUI 都能用类 DOM 数据结构去描述,引入 VNode 主要是将视图抽象化,提供了跨平台能力
- UI is a value :把视图当作一种变量值,能够进行编程化
- 基于虚拟 DOM 实现状态驱动的 UI 开发方式:避免了手动操作 DOM 效率低下以及规避 XSS 风险
vue 还提供很多的 VNode 类型:
// packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts
export type VNodeTypes =
| string // element
| VNode // slot
| Component // 组件
| typeof Text // 文本
| typeof Static // 静态
| typeof Comment // 注释
| typeof Fragment // 片段
| typeof TeleportImpl // 传送组件
| typeof SuspenseImpl // 挂载组件
export interface VNode<
HostNode = RendererNode,
HostElement = RendererElement,
ExtraProps = { [key: string]: any }
> {
type: VNodeTypes
props: (VNodeProps & ExtraProps) | null
children: VNodeNormalizedChildren
...
}
Vue 组件
组件是一种抽象概念、一种复用手段。
前端领域的组件化,即以视图为单位进行页面逻辑分割及复用,组件 = 视图模板 + 逻辑状态。
但是以这样的组件为基本复用单位,在前端领域你会发现很难复用。有时视图模板符合了但逻辑状态稍微得修改,代码只会加入更多的 case by case;有时逻辑状态符合了但模板样式却不符合 UI 需求,这就导致前端组件往往限于一定的场景。
最佳形式是组件是视图构成基本单位、视图模板与逻辑状态是最小复用单位 🤔。
基于 VirtualDOM 机制,组件本质上主要是对产生 vdom 的逻辑的封装。一个 Vue 组件的主要构成分层:

每一层的数据流依赖都是自顶向下:
- props/provide 外部对组件的输入
- setup(data) 组件内部逻辑组织、视图状态输出
- render 视图渲染,输出 vdom
- slots 对外部提供自定义渲染接口
基于 VirtualDOM 的组件渲染机制
无论是 Vue 或者 React,基于 VirtualDOM 的数据驱动框架原理基本有以下几个重要步骤:

- 数据变动(或者初始数据)
- Render:调度 Render 输出新 vdom
- Diff:
- Patch:执行系统平台对应的渲染命令
import { createVNode, patch, h } from "vue";
// 1. 组件定义
const CustomComponent = {
props: {
name: String,
},
setup(props) {
return {
resolveName: `hello ${props.name}`,
};
},
render() {
return h("div", [this.resolveName, this.$slots.default()]);
},
};
// 2. 创建组件的 vnode
const vnode = createVNode(
CustomComponent,
{ name: "world" },
{
default: "!",
}
);
// vnode
//{
// type: CustomComponent,
// props: {
// name: 'test'
// },
// children: '!'
//}
// 3. 渲染 vnode(patch vnode)
render(vnode, document.querySelector("#app"));
function render(vnode, container) {
// path 里会调用组件的 render,下面源码分析
// old vnode 初始为 null,意味这是初始渲染,执行挂载操作
patch(vnode, null, container)
}
// <div>hello world!</div>
vue 组件渲染流程源码分析
渲染流程分初始渲染和更新渲染,下面源码分析先从初始渲染流程。
创建应用对象
// 在 Vue3 中,一个 vue 应用创建标准流程如下
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './app'
const app = createApp(App)
app.mount('#app')
-------------------------------------------------------------
// runtime-dom 包中包含了 web 平台的渲染器
// packages/runtime-dom/src/index.ts
const createApp = ((...args) => {
// 1. 创建 web 渲染器、创建 app 对象
const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args)
const { mount } = app
// 重写 mount 方法
app.mount = (containerOrSelector) => {
const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector)
// 2. 调用 app.mount 核心标准方法,创建 vnode, 渲染 vnode
mount(container)
// ...
}
return app
})
渲染器 renderer
// packages/runtime-dom/src/index.ts
const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args); // 延迟创建渲染,方便 tree-shakable
// 创建自定义渲染器
// vue 为了跨平台支持,抽象标准化渲染器的平台渲染接口。
// renderer = createRenderer(nodeOps)
function ensureRenderer() {
return (
renderer || ((renderer = createRenderer < Node), Element > rendererOptions)
);
}
// 实现不同平台的渲染操作接口
const rendererOptions = extend({ patchProp, forcePatchProp }, nodeOps);
nodeOps(packages/runtime-dom/src/nodeOps.ts),实现了 web 平台下的渲染接口。通过创建自定义渲染器我们可以实现不同平台下的渲染。
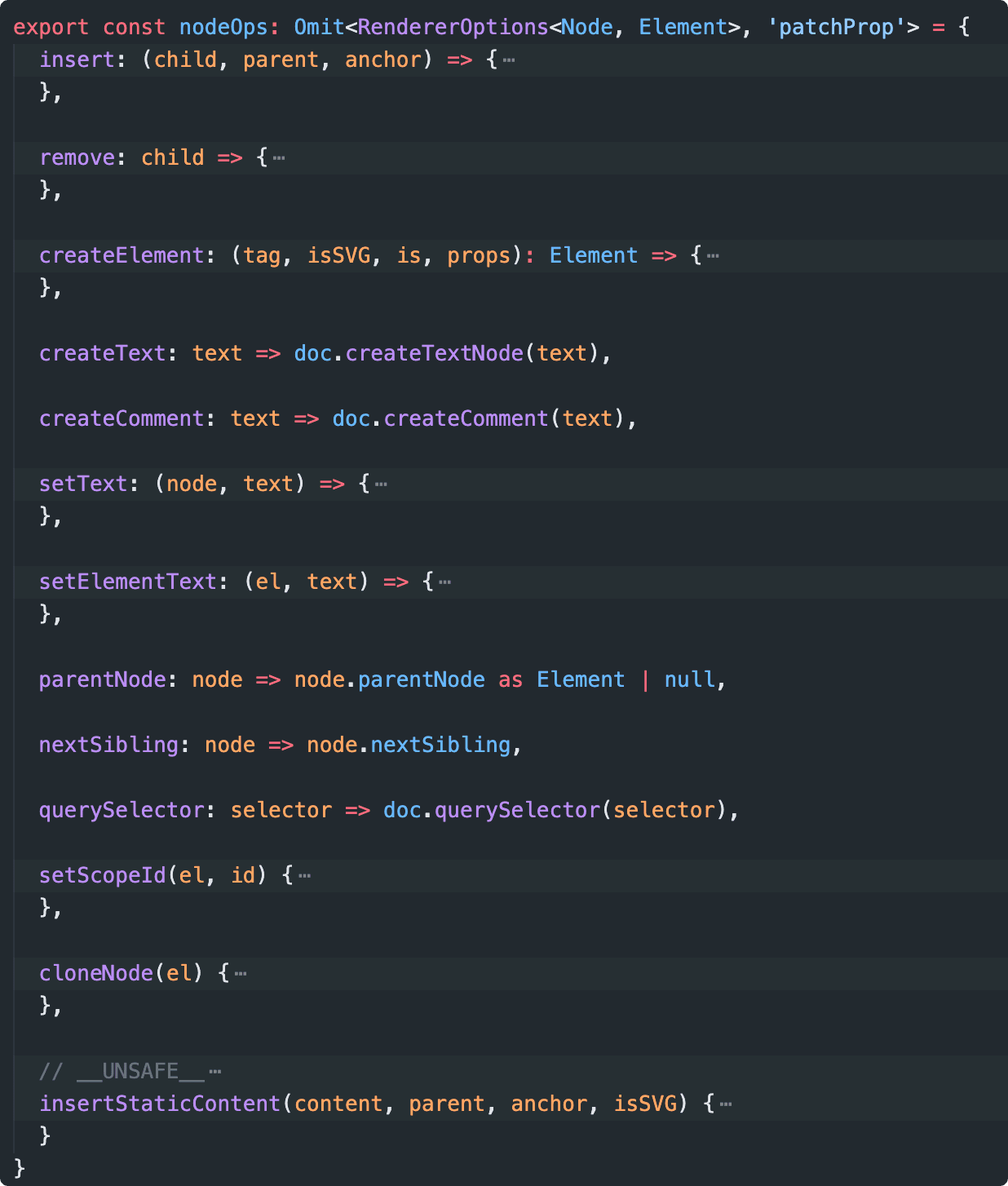
// packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts
// createRenderer 是 vue 自定义渲染器的核心方法
function createRenderer(nodeOps) {
return baseCreateRenderer(nodeOps);
}
function baseCreateRenderer(nodeOps) {
//接口定义
const remove: RemoveFn = (vnode) => {
// 接口调用
nodeOps.remove();
};
//...
// 利用闭包,将 nodeOps 保存下来
function render(vnode, container) {
// 组件渲染的核心逻辑
patch(vnode, container);
}
// 返回包含 render 方法的渲染器
return {
render,
// createAppAPI 创建 createApp
createApp: createAppAPI(render),
};
}
除了将渲染器跨平台渲染标准化,还将应用创建流程也标准化。
createAppAPI
相比以前使用插件、挂载全局属性方法都落到 Vue 构造函数和原型上,createApp 创建一个应用上下文,允许我们创建多个 vue 应用并进行全局配置隔离。
createApp 函数内部的 app.mount 方法是一个标准的跨平台的组件渲染流程:先创建 vnode,再渲染 vnode,生成 DOM。
// Vue.js 利用闭包和函数柯里化,createAppAPI 包装 render
function createAppAPI(render) {
// createApp createApp 方法接受的两个参数:根组件的对象和 prop
return function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null) {
const app = {
_component: rootComponent,
_props: rootProps,
mount(rootContainer) {
// 创建根组件的 vnode
const vnode = createVNode(rootComponent, rootProps);
// 调用渲染器的 render vnode
render(vnode, rootContainer);
app._container = rootContainer;
return vnode.component.proxy;
},
};
return app;
};
}
这里的代码的执行逻辑都是与平台无关的,启动标准渲染流程。如果有需要可以在外部重写这个方法,来完善特定平台下的渲染逻辑。
比如 web 平台:
// packages/runtime-dom/src/index.ts
const { mount } = app
app.mount = (containerOrSelector: Element | ShadowRoot | string): any => {
// 标准化 root el 获取
const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector)
if (!container) return
const component = app._component
// 支持 html root 元素作为 template
if (!isFunction(component) && !component.render && !component.template) {
// __UNSAFE__
// Reason: potential execution of JS expressions in in-DOM template.
// The user must make sure the in-DOM template is trusted. If it's
// rendered by the server, the template should not contain any user data.
component.template = container.innerHTML
}
// clear content before mounting
// 清除 root 内容
container.innerHTML = ''
const proxy = mount(container, false, container instanceof SVGElement)
if (container instanceof Element) {
container.removeAttribute('v-cloak')
container.setAttribute('data-v-app', '')
}
return proxy
}
进入应用挂载阶段后,接下来就是核心的组件渲染流程。
组件渲染
创建 vnode
// packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts
function _createVNode(
type: VNodeTypes | ClassComponent | typeof NULL_DYNAMIC_COMPONENT,
props: (Data & VNodeProps) | null = null,
children: unknown = null,
patchFlag: number = 0,
dynamicProps: string[] | null = null,
isBlockNode = false
): VNode {
if (props) {
// 处理 props 相关逻辑,标准化 class 和 style
}
// 对 vnode 类型信息编码
// 以便在后面的 patch 阶段,可以根据不同的类型执行相应的处理逻辑
const shapeFlag = isString(type)
? ShapeFlags.ELEMENT
: __FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && isSuspense(type)
? ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE
: isTeleport(type)
? ShapeFlags.TELEPORT
: isObject(type)
? ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
: isFunction(type)
? ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT
: 0
const vnode: VNode = {
type,
props,
key: props && normalizeKey(props),
...
}
// 标准化子节点,把不同数据类型的 children 转成数组或者文本类型
normalizeChildren(vnode, children)
return vnode
}
工厂模式创建 vnode,并且对 props、children 做标准化处理、对 vnode 的 type、children 做信息编码,以便在后面可以根据不同的类型执行相应的处理逻辑。
渲染 vnode(patch vnode)
const render: RootRenderFunction = (vnode, container, isSVG) => {
if (vnode == null) {
// 销毁组件
if (container._vnode) {
unmount(container._vnode, null, null, true);
}
} else {
// 创建或者更新组件
patch(container._vnode || null, vnode, container, null, null, null, isSVG);
}
// 缓存 vnode 节点,表示已经渲染
container._vnode = vnode;
};
patch 会根据不同的 vnode 类型派发任务给 process 处理。但初始渲染时旧 vnode 为 null,最终处理结果基本是 mount 操作:
diff type => process => mount
比如根 vnode 是个组件类型,故 processComponent 进行处理,调用 mountComponent 方法渲染组件。
const patch: PatchFn = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor = null,
parentComponent = null,
parentSuspense = null,
isSVG = false,
slotScopeIds = null,
optimized = false
) => {
// 如果存在新旧节点, 且新旧节点类型不同,则销毁旧节点
if (n1 && !isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
anchor = getNextHostNode(n1)
unmount(n1, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
n1 = null
}
const { type, ref, shapeFlag } = n2
switch (type) {
case Text:...
case Comment:...
case Static:...
case Fragment:...
default:
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
...
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) {
processComponent(
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) {
...
} else if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) {
...
} else if (__DEV__) {
...
}
}
const processComponent = (n1, n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized) => {
if (n1 == null) {
// 挂载组件
mountComponent(n2, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized)
}
else {
// 更新组件
updateComponent(n1, n2, parentComponent, optimized)
}
}
// 挂载组件
const mountComponent = (initialVNode, container, anchor, parentComponent, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized) => {
// 创建组件实例
const instance = (initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(initialVNode, parentComponent, parentSuspense))
// 初始化 Props、Slots、调用 setup 初始状态
setupComponent(instance)
// 设置并运行渲染副作用
setupRenderEffect(instance, initialVNode, container, anchor, parentSuspense, isSVG, optimized)
}
mountComponent 方法渲染组件中最主要的是 setupRenderEffect,该函数利用响应式库的 effect 函数创建了一个组件的渲染副作用。在响应式系统下,当组件的数据发生变化时,effect 函数包裹的组件渲染函数会重新执行一遍,从而达到重新渲染组件的目的。
const setupRenderEffect = (
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
// 创建响应式的副作用渲染函数
instance.update = effect(function componentEffect() {
if (!instance.isMounted) {
// 调用组件的 render 方法,生成 subTree
const subTree = (instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance));
// patch subTree
patch(null, subTree, container, anchor, instance, parentSuspense, isSVG);
// 保留渲染生成的子树根 DOM 节点
initialVNode.el = subTree.el;
instance.isMounted = true;
} else {
// 更新组件
}
}, prodEffectOptions);
// 初始渲染
instance.update();
};
组件在 vnode tree 中只是个抽象节点,实际渲染的是组件的 render 函数生成 subTree,故还要继续 patch subTree。
经过 patch 函数的深度递归处理,普通元素类型的节点处理才会是最终反应到页面上。
// patch => processElement => mountElement
const mountElement = (
vnode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
optimized
) => {
let el;
const { type, props, shapeFlag } = vnode;
// 创建 DOM 元素节点
el = vnode.el = hostCreateElement(vnode.type, isSVG, props && props.is);
if (props) {
// 处理 props,比如 class、style、event 等属性
for (const key in props) {
if (!isReservedProp(key)) {
hostPatchProp(el, key, null, props[key], isSVG);
}
}
}
if (shapeFlag & 8 /* TEXT_CHILDREN */) {
// 处理子节点是纯文本的情况
hostSetElementText(el, vnode.children);
} else if (shapeFlag & 16 /* ARRAY_CHILDREN */) {
// 处理子节点是数组的情况
mountChildren(
vnode.children,
el,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG && type !== "foreignObject",
optimized || !!vnode.dynamicChildren
);
}
// 把创建的 DOM 元素节点挂载到 container 上
hostInsert(el, container, anchor);
};
在 mountElement 方法调用平台渲染方法,比如 hostCreateElement,在 web 平台底层就是调用 document.createElement 方法。
深度递归 vnode tree 的过程,挂载的顺序是先子节点,后父节点,最终挂载到最外层的容器上,完成整个渲染流程。
总结
- 创建应用 createApp,可以让我们进行应用环境隔离
- 组件 vnode 是抽象节点,是不会生成真实节点,调用组件模板生成 subTree 去渲染
- 元素类型的节点才会最终落实渲染成真实 DOM 节点
- VirtualDOM 的渲染机制就是深度递归 diff 新旧 vnode tree 差异并调用平台的渲染接口,生成真实的 DOM
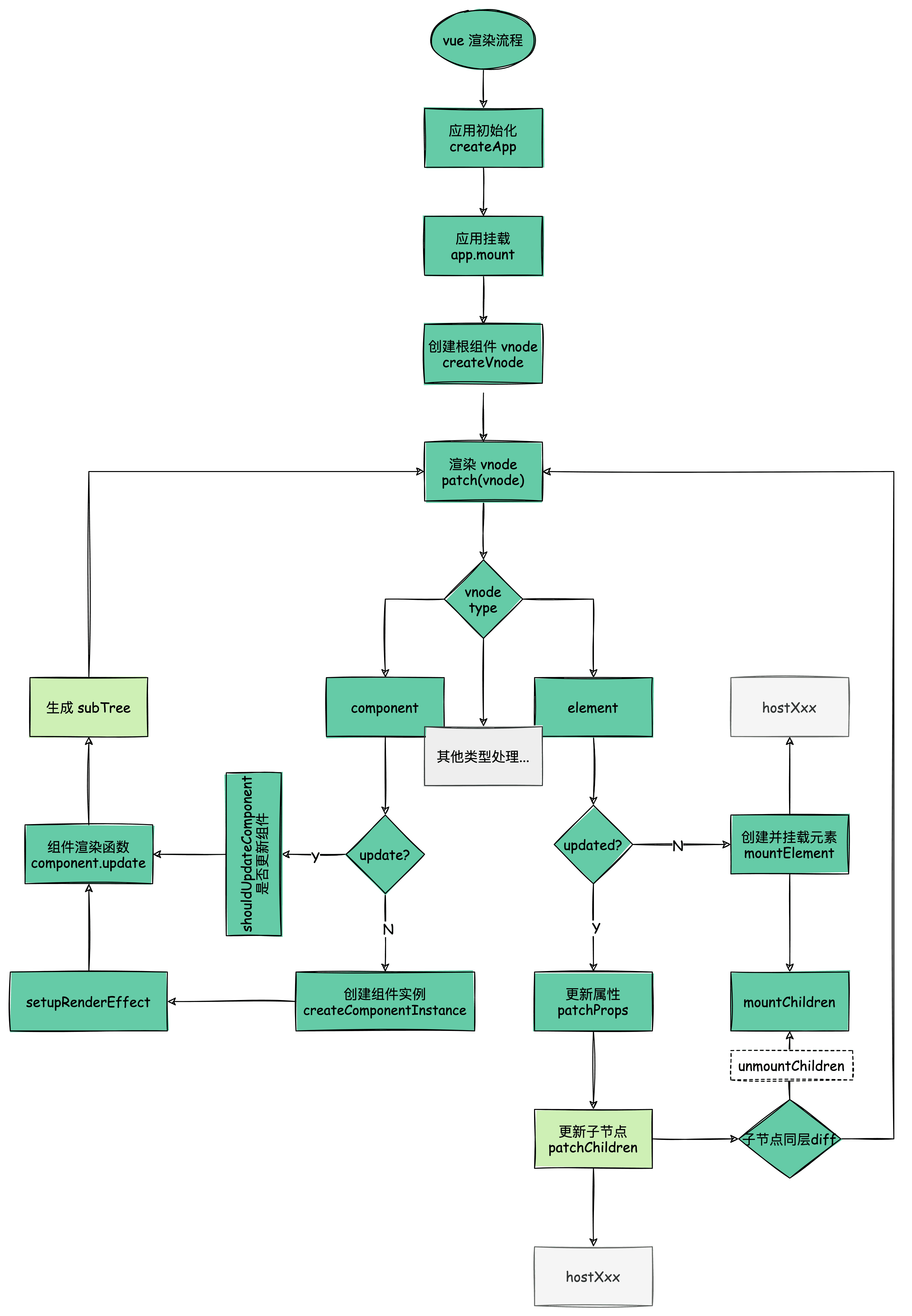
下图为 vue 渲染流程,其中更新流程也包括在里面